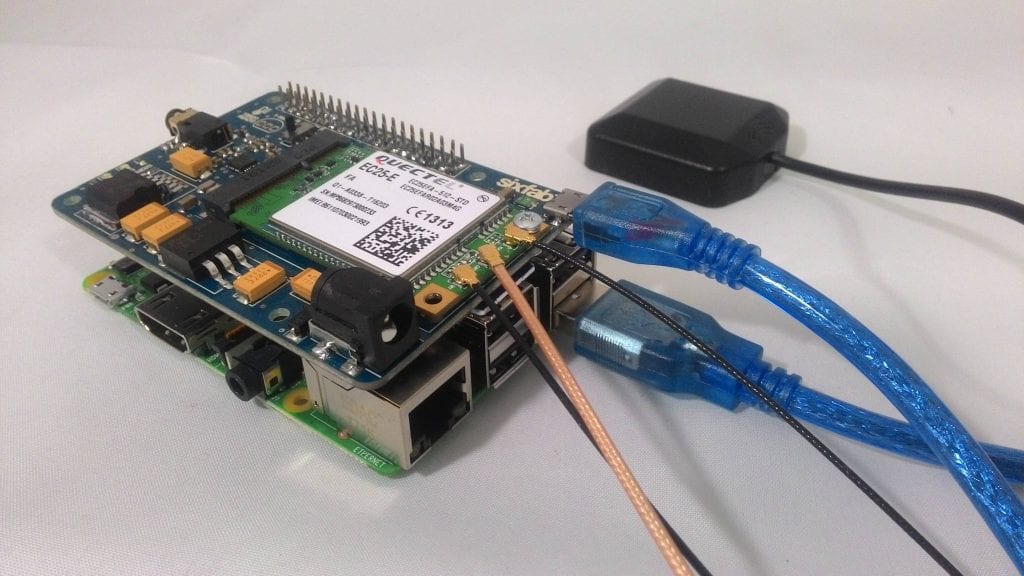
In this tutorial we will learn how to get GPS data using 3G, 4G/LTE shield.
GPS(Global Positioning System) also known as NavStar indicates the position of an individual on the earth. The Satellites orbiting around the earth sends precise details of their positions at a regular interval of time. Once information are received by a GPS receiver, a GPS receiver can pinpoint the location.
There are also navigation systems which support in their in specific regions like GLONASS provided in Russia.
For this tutorial we will need
a. Raspberry Pi
b. 3G, 4G/LTE Shield
c. 3G, 4G/LTE module (for 3G UC20 and for 4G EC25 is used)
d. PCB Mobile Antenna (2x)
e. GPS Antenna
Here it goes
1. Connect EC25 module to the shield.
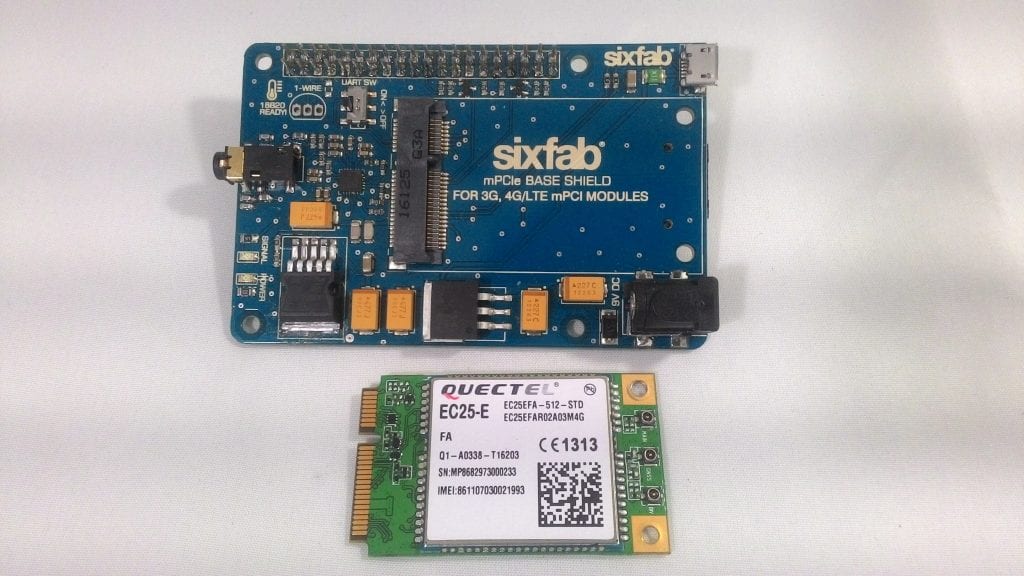

Sixfab 3G,4G/LTE shield and EC25 module
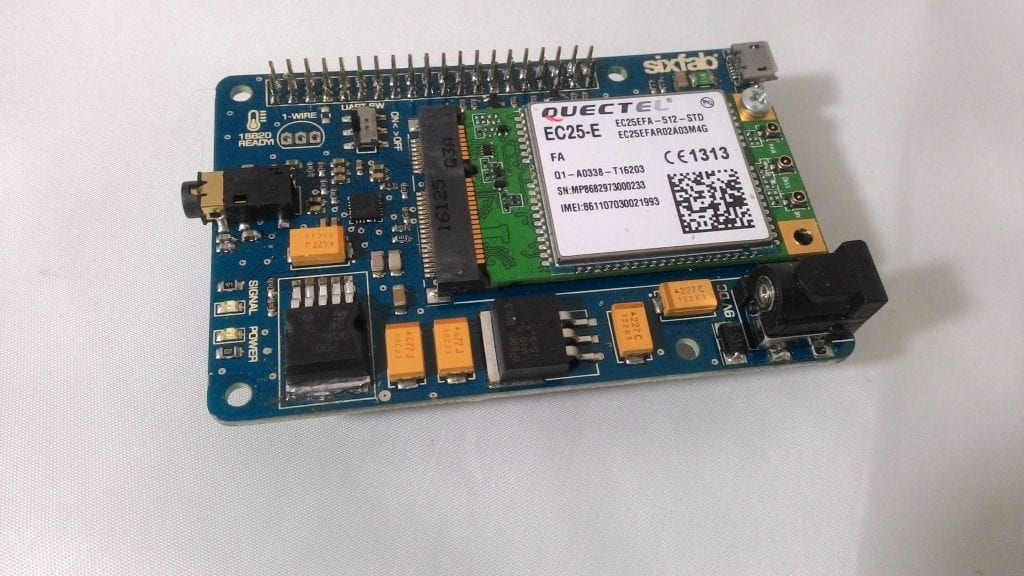

EC25 module connected to shield
2. Insert SIM in the sim slot
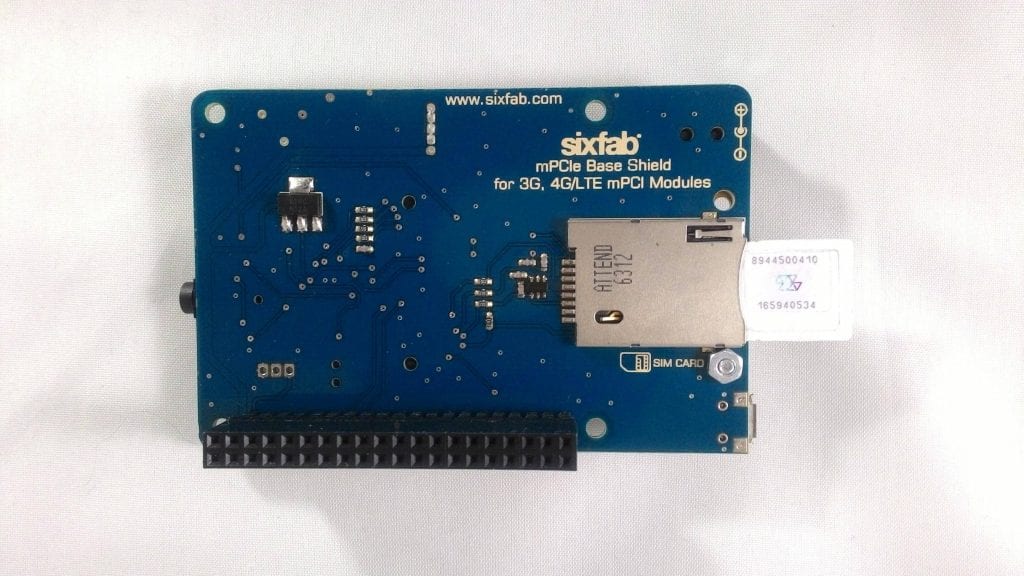
Inserting Sim
3. Connect the shield to a Raspberry Pi
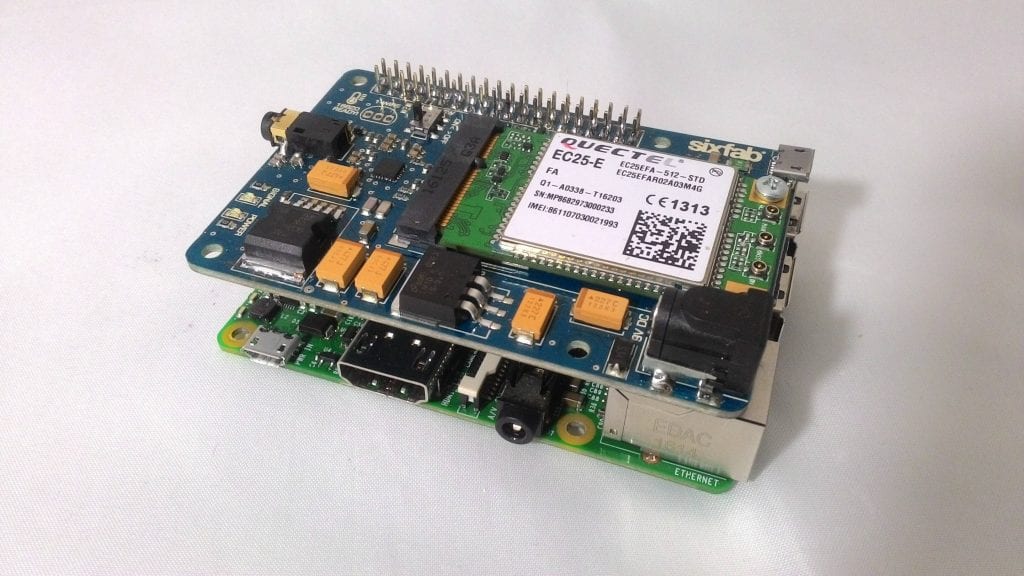

Shield attached to Raspberry Pi 3
4. Now connect antenna to the ports as shown in the figure below
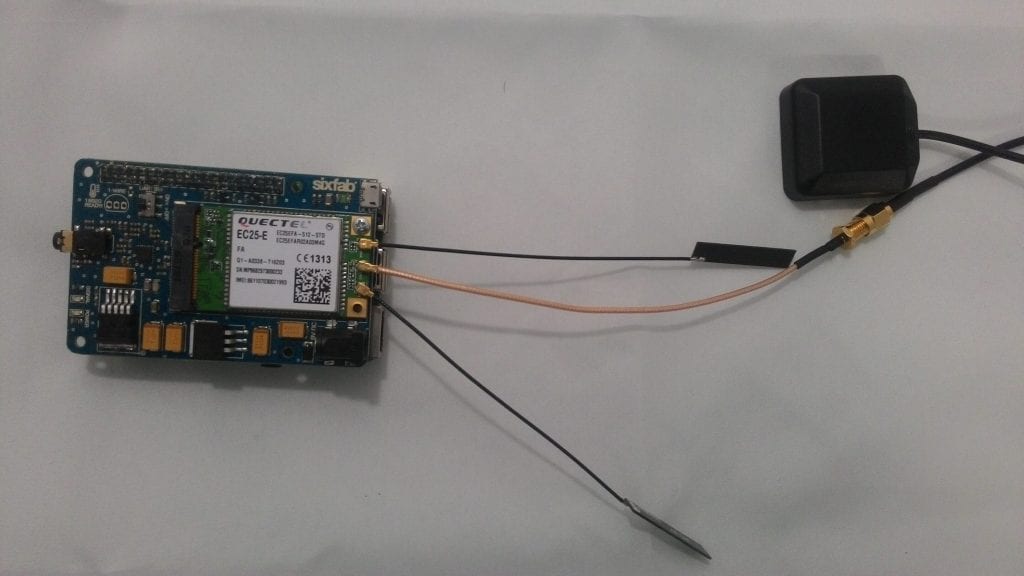

Connecting Antenna
5. Now connect a microUSB to the shield from Raspberry Pi.
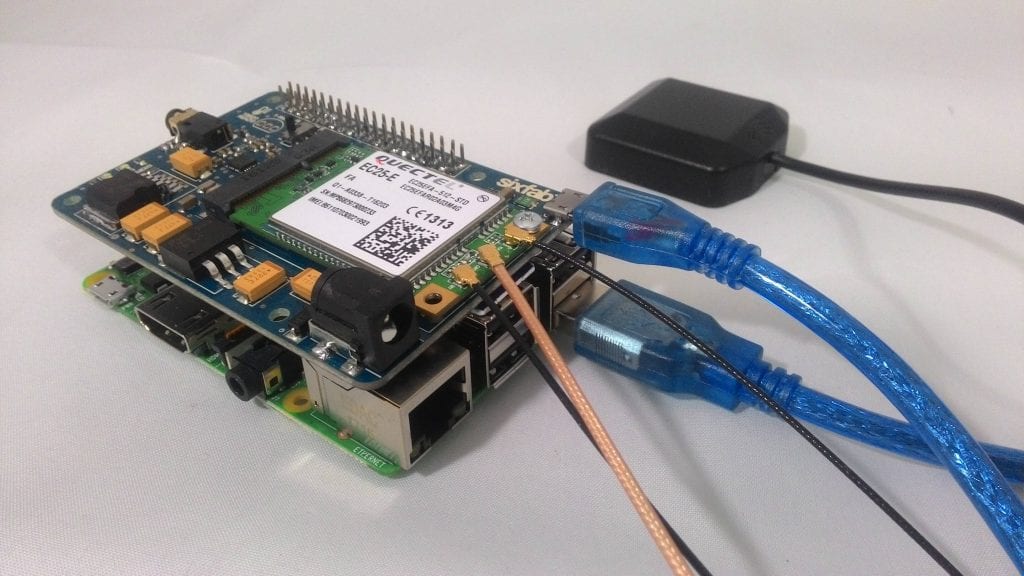

Tracker setup
So the setup is ready for tracking.
Now we can power our Raspberry Pi and control trough terminal as done in previous tutorials.
GPS data can be obtained either using minicom or writing your own python code.
***************************************MINICOM***************************************
6a. Type
minicom -s
to bring up the minicom settings screen
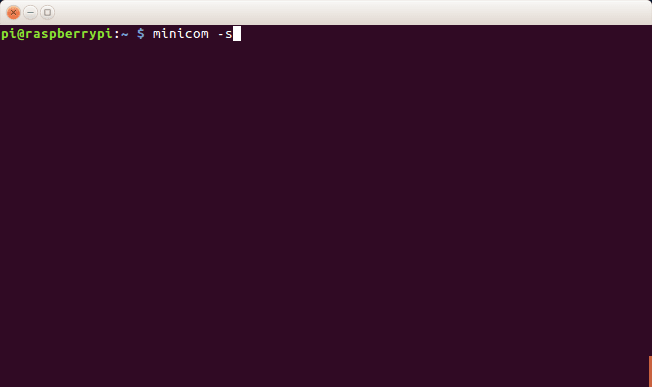 Opening minicom
Opening minicom
6b. Select Serial port setup
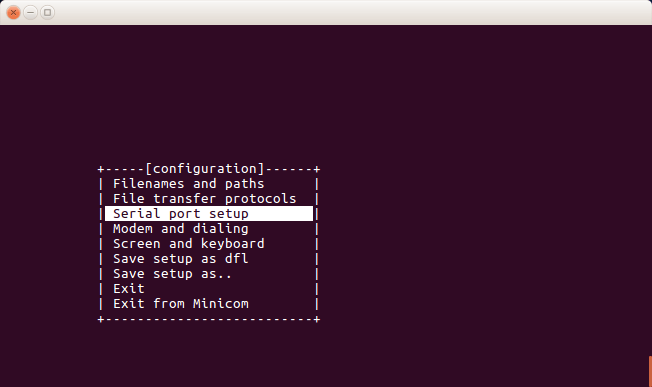
minicom configuration screen
6c. Make the following changes
Serial Device : /dev/ttyUSB2
Hardware Flow Control : No
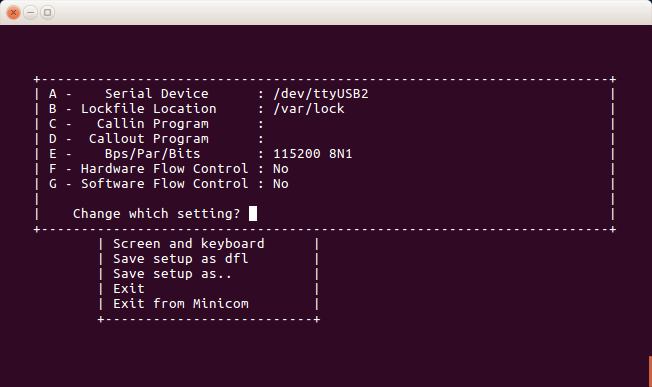
Configuring Serial Port Setup
6d. Now Exit from the setting screen
Exiting from minicom configuration screen
6e. Check connectivity with ‘AT’ which in response gives ‘OK’ or returns an error.
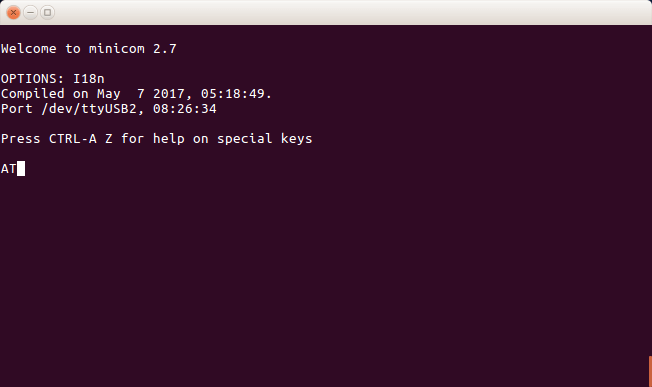
minicom screen
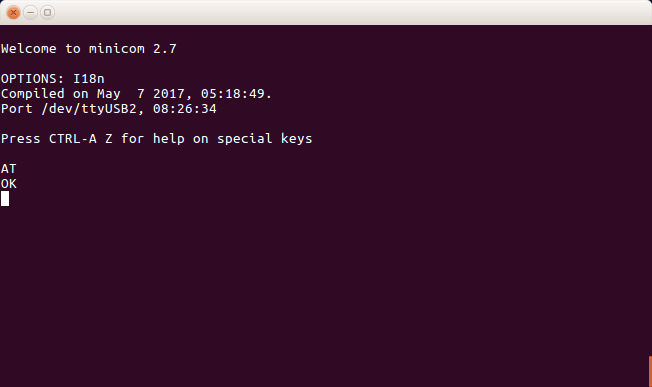
minicom screen
6f. Now type ‘AT+QGPS=1’ turns on the GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite Systems) engine.
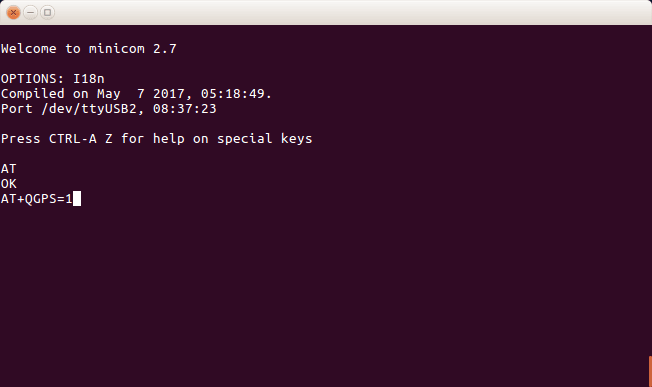
minicom screen
6g. Again go to minicom settings > Serial Port Setup and make the following changes.
Serial device : /dev/ttyUSB1
Hardware Flow Control : No
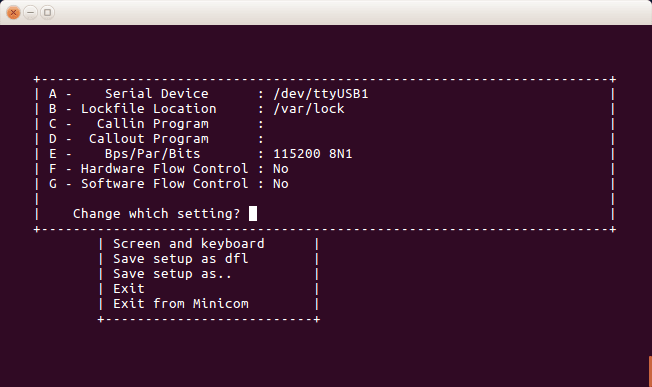
Configuring Serial Port Setup
6h. Exit from the settings screen which will bring up following screen with GPS NMEA data.
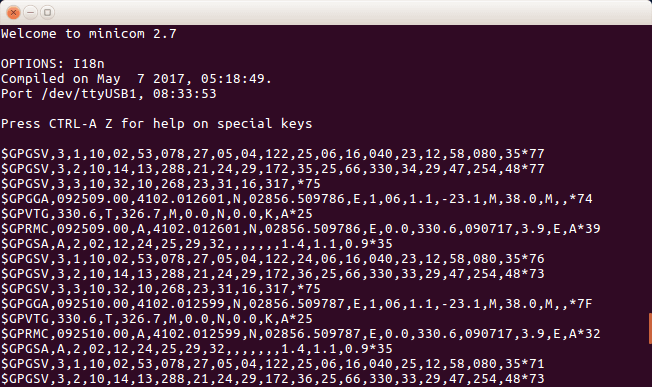
GPS Data
****************************************************Pyhton****************************************************
Now we will write a python code to obtain the GPS values
7a. First create a python file by the following command.
sudo nano gpstest.py
Opening .py file
7b. Now type the following python code in the file and save it. You may get the code from github.
from time import sleep
import serial
portwrite = "/dev/ttyUSB2"
port = "/dev/ttyUSB1"
def parseGPS(data):
print "raw:", data #prints raw data
if data[0:6] == "$GPRMC":
sdata = data.split(",")
if sdata[2] == 'V':
print "no satellite data available"
return
print "-----Parsing GPRMC-----"
time = sdata[1][0:2] + ":" + sdata[1][2:4] + ":" + sdata[1][4:6]
lat = decode(sdata[3]) #latitude
dirLat = sdata[4] #latitude direction N/S
lon = decode(sdata[5]) #longitute
dirLon = sdata[6] #longitude direction E/W
speed = sdata[7] #Speed in knots
trCourse = sdata[8] #True course
date = sdata[9][0:2] + "/" + sdata[9][2:4] + "/" + sdata[9][4:6]
#date
variation = sdata[10] #variation
degreeChecksum = sdata[11]
dc = degreeChecksum.split("*")
degree = dc[0] #degree
checksum = dc[1] #checksum
print "time : %s, latitude : %s(%s), longitude : %s(%s), speed : %s, True Course : %s, Date : %s, Magnetic Variation : %s(%s),Checksum : %s "% (time,lat,dirLat,lon,dirLon,speed,trCourse,date,variation,degree,checksum)
else:
print "Printed data is ",data[0:6]
def decode(coord):
#Converts DDDMM.MMMMM -> DD deg MM.MMMMM min
x = coord.split(".")
head = x[0]
tail = x[1]
deg = head[0:-2]
min = head[-2:]
return deg + " deg " + min + "." + tail + " min"
print "Connecting port"
serw = serial.Serial(portwrite, baudrate = 115200, timeout = 1)
serw.write('AT+QGPS=1\r')
serw.close()
sleep(0.5)
print "Receiving GPS data"
ser = serial.Serial(port, baudrate = 115200, timeout = 0.5)
while True:
data = ser.readline()
parseGPS(data)
7c. After saving it we will run the code with following command.
sudo python gpstest.py
Running .py file
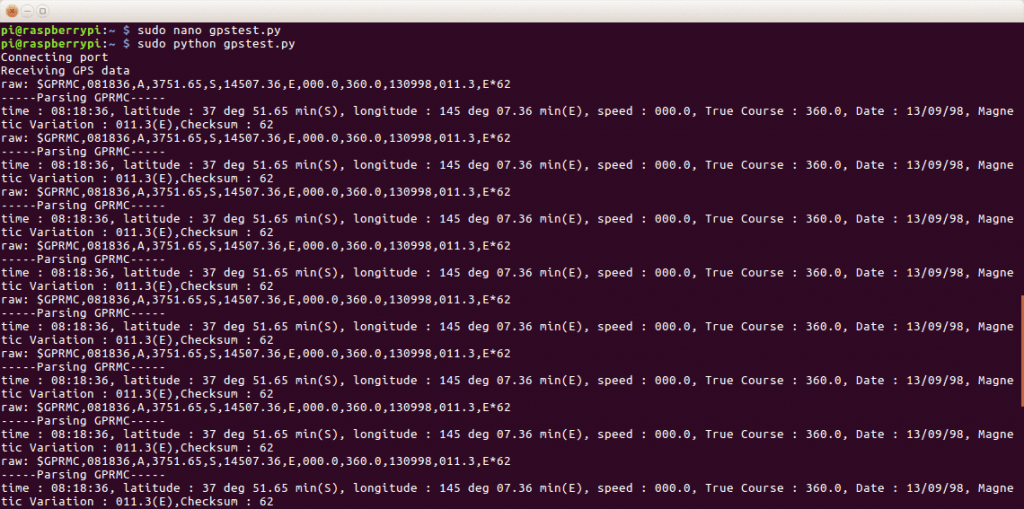
GPS data received
Similarly depending on the code required values from the data can be extracted.