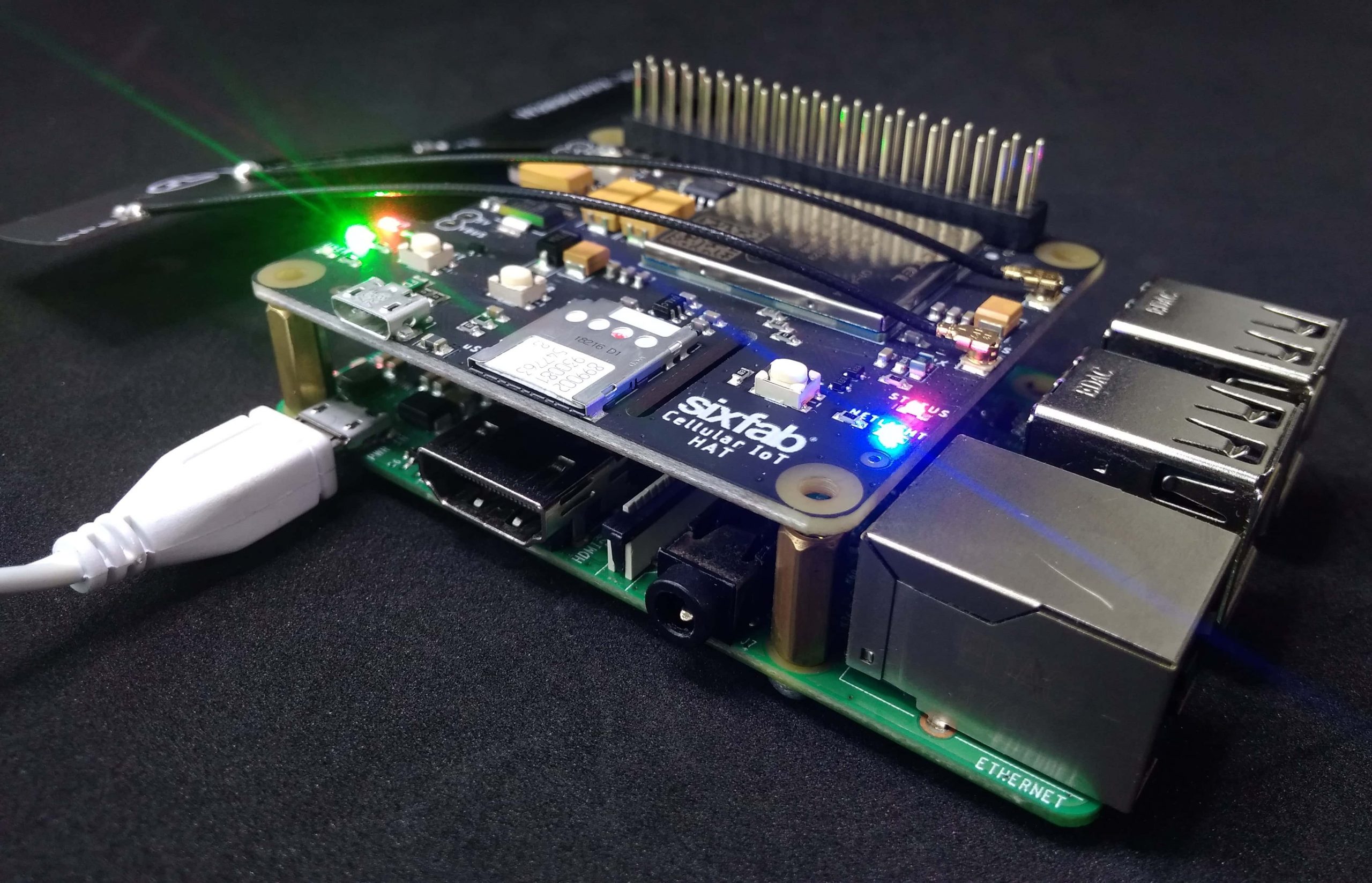
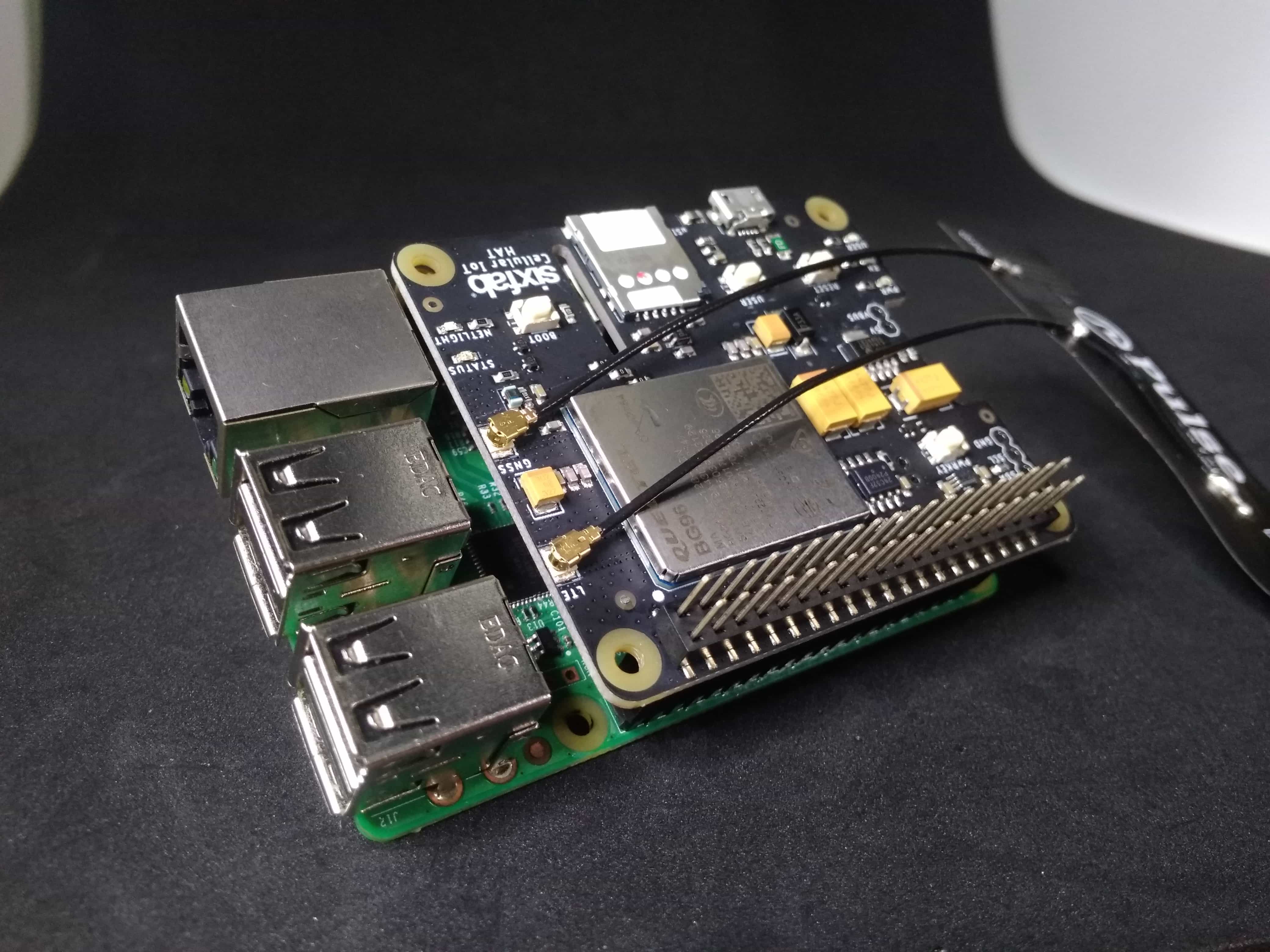
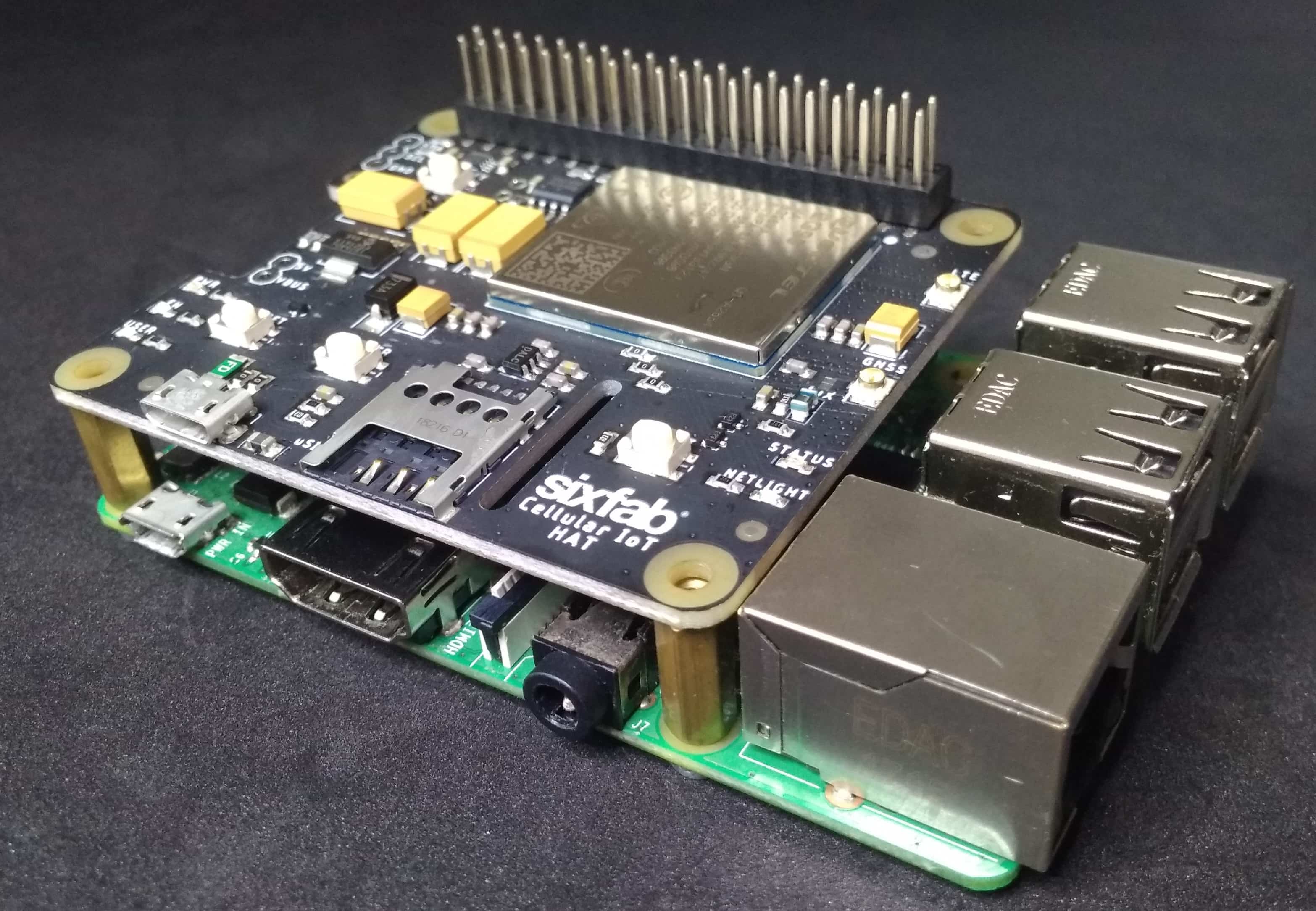
Sixfab came up with Raspberry Pi Cellular IoT HAT. This time it is a Hat rather than a shield. To be more specific this HAT is lighter version of our previous Raspberry Pi Cellular IoT Application Shield, where both uses Quectel BG96 module. The major difference is the peripheral sensors, the HAT doesn’t contain any sensors on it.
What is the feature of this HAT?
This HAT contains Quectel BG96 which has combined LTE technologies Cat.M1, Cat.NB1 and eGPRS.
It also supports GPS.
Preconfiguration
Before we start working with the HAT, let us setup our router settings and Raspberry pi.
Your router needs port forwarding for UDP connection. Note down the IP address of your router and UDP port number.
The Serial port hardware of your Raspberry Pi should be enabled and Login shell to be accessible over serial should be disabled. This can be done from raspi-config.
Hardware Setup
-
- Attach the Cellular IoT HAT to your Raspberry Pi.

- Attach the Cellular IoT HAT to your Raspberry Pi.
-
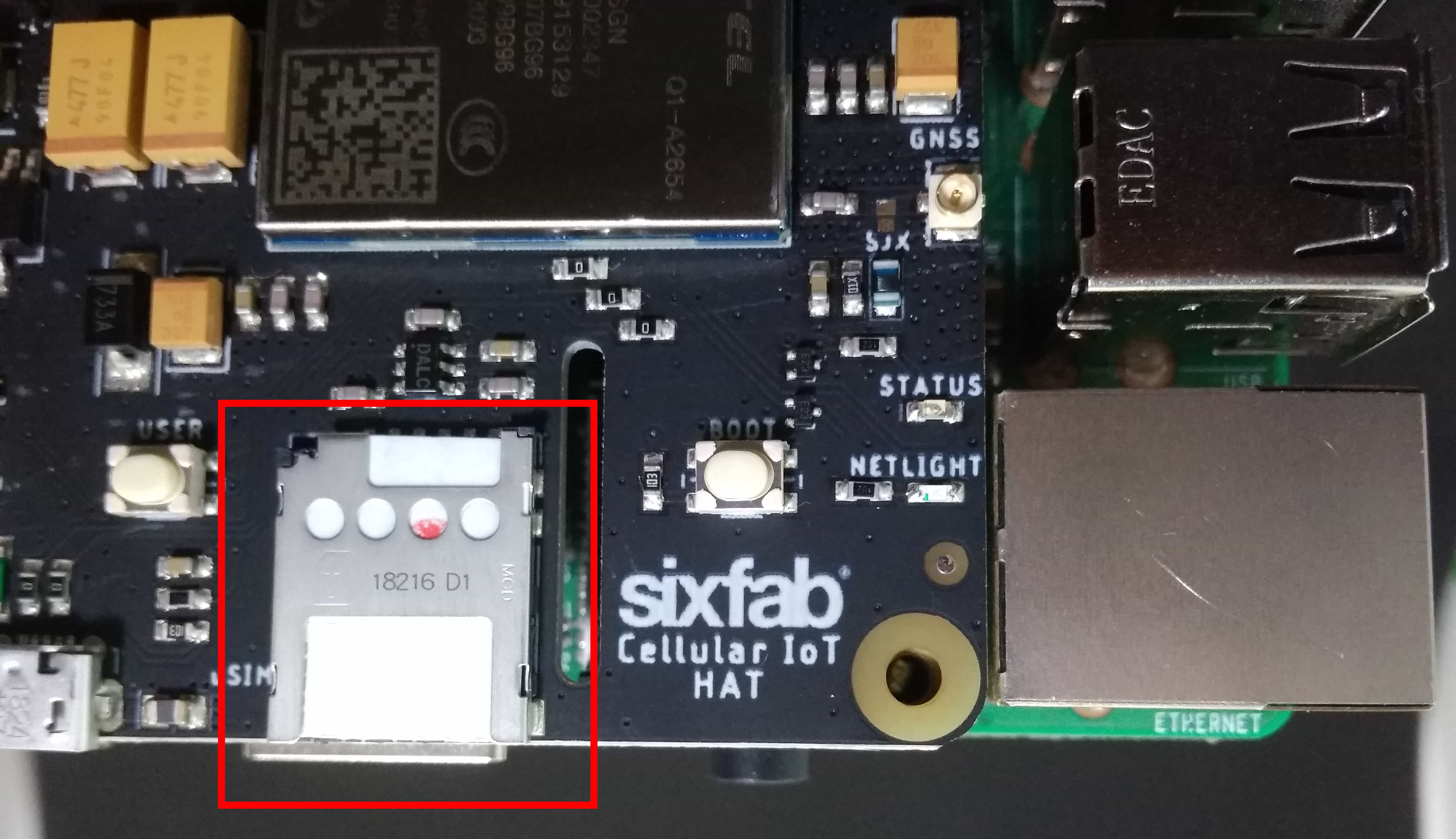
- Insert the Sim.

- Insert the Sim.
-
- Plug the antenna. You will need one LTE antenna with u.FL for this tutorial. Here, I am using LTE Full Band PCB Antenna.

- Plug the antenna. You will need one LTE antenna with u.FL for this tutorial. Here, I am using LTE Full Band PCB Antenna.
Software Setup
Now we are ready to start.
-
- Download/clone the library from github
git clone https://github.com/sixfab/Sixfab_RPi_CellularIoT_App_Shield.git

- Download/clone the library from github
-
- Now get into the cloned directory.
cd Sixfab_RPi_CellularIoT_Library

- Now get into the cloned directory.
-
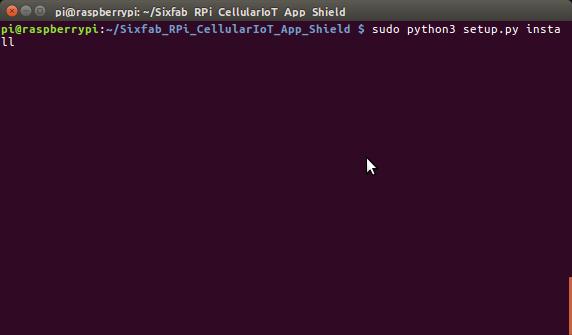
- Now install the library
sudo python3 setup.py install
Make sure you are installing it with python3.

- Now install the library
-
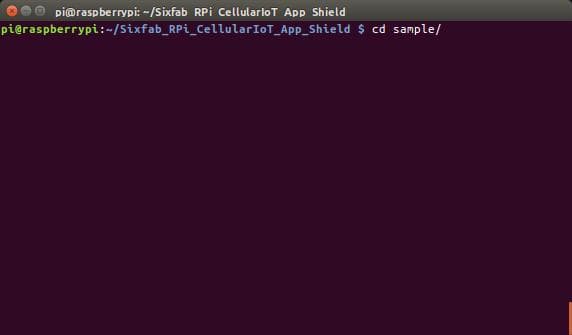
- Now goto sample directory
cd sample/

- Now goto sample directory
-
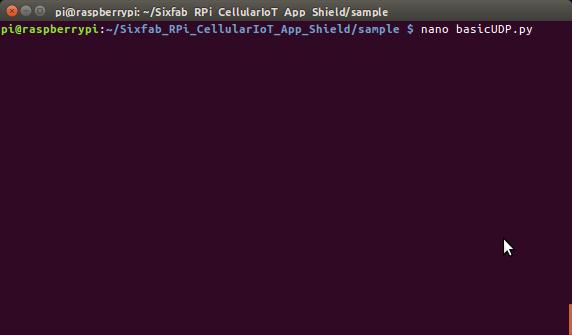
- Now open the basicUDP.py script.
nano basicUDP.py

- Now open the basicUDP.py script.
-
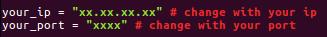
- Here, you will see following two lines.
your_ip = "xx.xx.xx.xx"; your_port = "xxxx";You have to replace these information with your own which have set in the preconfiguration step that is the routers IP and the UDP port address.

- Here, you will see following two lines.
-
- Check if the
node = cellulariot.CellularIoT()is uncommented.

- Check if the
-
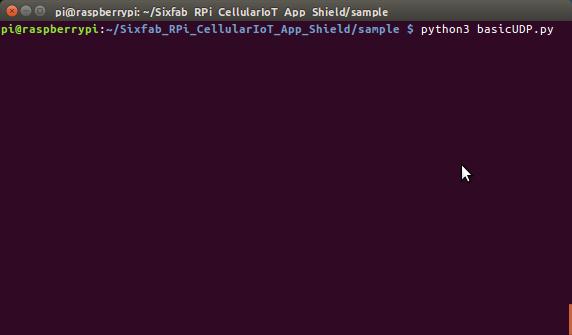
- Now save the python script and run with
python3 basicUDP.py

- Now save the python script and run with
-
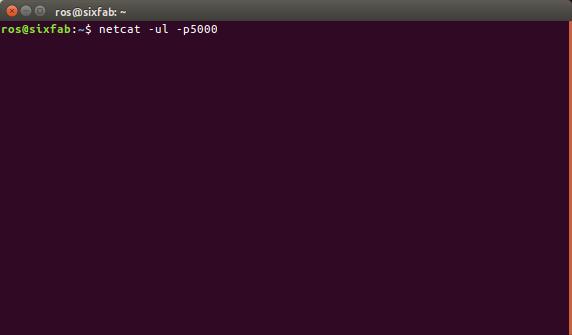
- Just before running the script open a new terminal in your laptop and type
netcat -ul -p5000
Here 5000 is my port number. Replace it with your port number. (This is to be done in the Device where you have directed the UDP port during the preconfiguration step)

- Just before running the script open a new terminal in your laptop and type
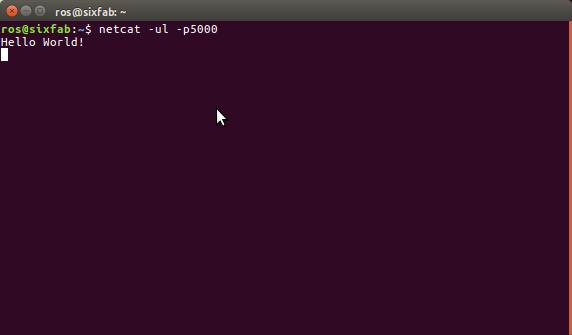
- Here you can see the Data that has been sent over UDP.

Hence, We are done with the tutorial here. Please write suggestions, questions and feedback in the comment section below.